Diamond Color vs. Diamond Clarity | Which one is more important?
Diamonds have long been revered for their unparalleled beauty and timeless elegance. When it comes to selecting a diamond, understanding the significance of diamond color and diamond clarity is crucial. In this article, we explore the intricacies of these two factors and their respective impacts on a diamond’s appearance. By delving into the depths of diamond color and diamond clarity, readers will gain valuable insights to make well-informed choices.
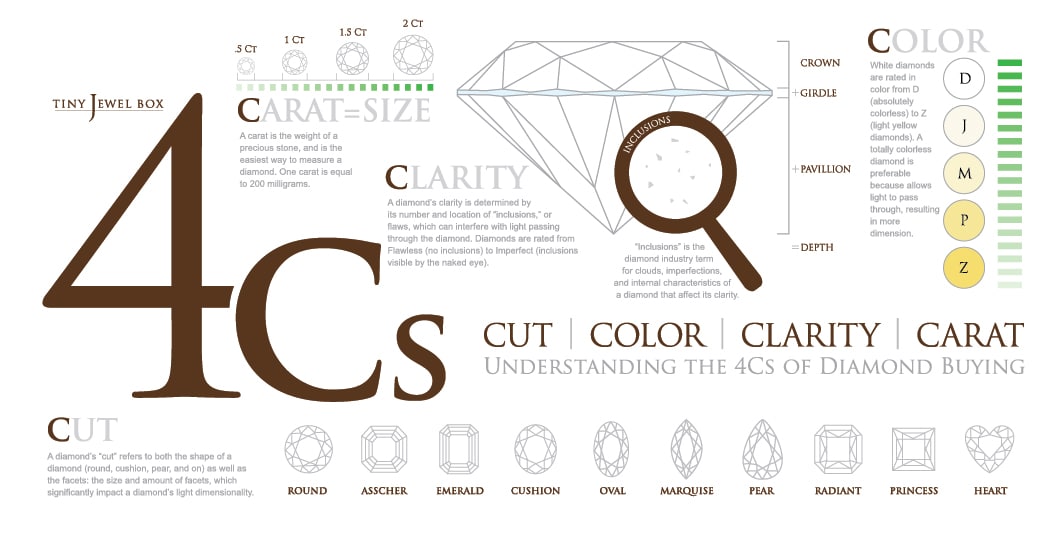
How Diamond Color Affects Appearance
Diamond color plays a vital role in determining a diamond’s visual appeal. The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) grades diamond color on a scale from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown). A higher color grade signifies a diamond with minimal or no detectable color.

The absence of color allows light to pass through the diamond with ease, resulting in exceptional brilliance and fire. Diamonds with higher color grades (D-F) are highly sought after for their icy white or colorless appearance, reflecting maximum light and showcasing a stunning visual impact.
FAQs about Diamond Color
Q1. Are slight color differences noticeable to the naked eye?
A: In most cases, the human eye may not detect subtle color variations between adjacent color grades. However, color differences become more apparent as you move down the color scale, making lower color grades (G-J) exhibit a hint of warmth or a slight yellowish hue.
Q2. Can diamond shape affect the perception of color?
A: Yes, the shape of a diamond can influence how color is perceived. Certain diamond cuts, such as the round brilliant cut, tend to mask color better than other cuts. The facets and angles of the cut can enhance a diamond’s brilliance and disguise any potential color tints.
How Diamond Clarity Affects Appearance
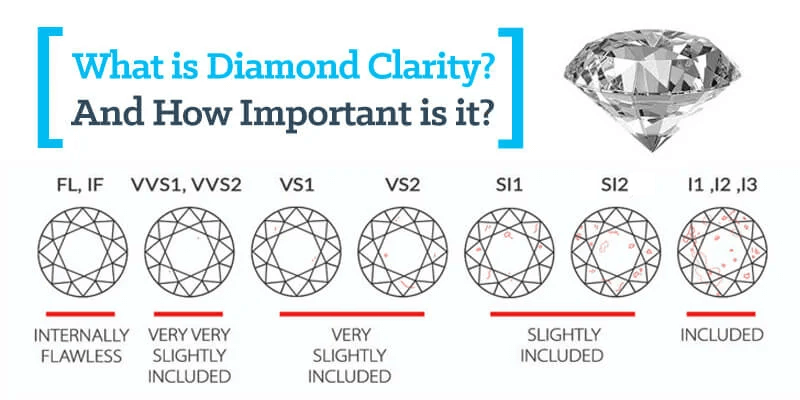
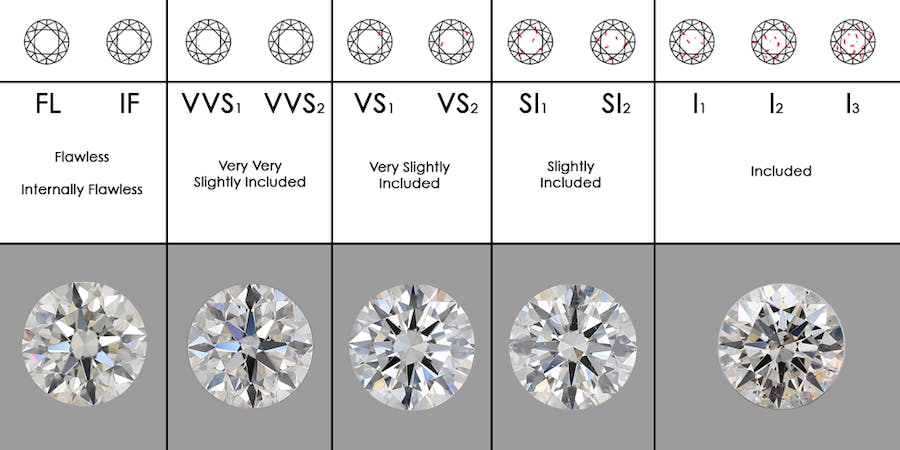
Diamond clarity refers to the presence of internal characteristics (inclusions) and external blemishes. The GIA grades diamond clarity on a scale ranging from Flawless (no visible inclusions or blemishes under 10x magnification) to Included (visible inclusions to the naked eye).
Higher clarity grades (IF-VVS) indicate diamonds with exceptional transparency and minimal inclusions. These diamonds exhibit maximum brilliance, as light passes through them without obstructions, resulting in captivating sparkle.
FAQs about Diamond Clarity
Q1. Are inclusions visible to the naked eye?
A: Inclusions are often microscopic and may not be visible to the naked eye. The majority of diamonds contain some form of inclusions, but their visibility depends on their size, location, and the overall clarity grade. Diamonds with higher clarity grades typically have fewer or less visible inclusions.
Q2. Can inclusions affect a diamond’s durability?
A: Inclusions are natural characteristics of diamonds formed deep within the Earth. While they may impact a diamond’s clarity, they rarely affect its durability. It’s crucial to choose a diamond with a clarity grade that ensures the stone’s structural integrity is not compromised.
Which is More Important: Diamond Color or Diamond Clarity?
Determining the importance of diamond color versus diamond clarity is subjective and depends on individual preferences and priorities. However, it is generally recommended to strike a balance between the two.
Diamond color often has a more noticeable impact on a diamond’s overall appearance. A higher color grade can create a brilliant, colorless effect that many individuals seek in a diamond. However, it’s important to consider other factors, such as the diamond’s shape, cut, and size, as they can influence the perception of color.
Diamond clarity, while less immediately visible, contributes to a diamond’s transparency and ability to reflect light. Higher clarity grades ensure exceptional brilliance, as light passes through the stone unimpeded. However, it’s worth noting that many inclusions are microscopic and may not affect the diamond’s beauty or durability.
The Importance of Diamond Color vs. Diamond Clarity
When it comes to determining which characteristic holds greater importance, it largely depends on personal preference and the desired visual effect. While both color and clarity contribute significantly to a diamond’s appearance, their impact varies based on individual taste and the design of the jewelry piece.
Diamond color, with its ability to influence the stone’s whiteness or colorlessness, often plays a more perceptible role in a diamond’s visual appeal.The color of a diamond is one of the first things that catches the eye, and a higher color grade can enhance the stone’s overall brilliance and beauty. However, it’s essential to consider other factors such as the diamond’s shape, cut, and size, as they can also influence how color is perceived. For example, certain diamond cuts may hide color better than others, allowing you to choose a slightly lower color grade without compromising the stone’s visual impact.
On the other hand, diamond clarity, while less immediately noticeable, can significantly affect a diamond’s transparency and ability to reflect light. Higher clarity grades ensure that light can pass through the stone without obstruction, resulting in exceptional brilliance and scintillation. However, it’s important to note that inclusions are often microscopic and may not be visible to the naked eye. Therefore, a diamond with a slightly lower clarity grade may still appear flawless when viewed without magnification.
Ultimately, the choice between diamond color and diamond clarity boils down to personal preference and budget considerations. If you value a bright, colorless appearance and desire a diamond that showcases exceptional brilliance, a higher color grade may be more important to you. Conversely, if you appreciate uniqueness and are open to a warm or slightly tinted diamond, you might prioritize a lower color grade and invest in higher clarity to ensure maximum sparkle.
Conclusion
Diamond color and diamond clarity are both important considerations when selecting a diamond, as they significantly affect its appearance. Diamond color grades influence the stone’s whiteness or colorlessness, with higher grades reflecting a brilliant and colorless beauty. Diamond clarity grades determine the visibility of internal and external flaws, with higher grades ensuring exceptional transparency and brilliance.
While the importance of diamond color versus diamond clarity is subjective, it is crucial to strike a balance between the two factors and consider other elements such as cut, shape, and size. By doing so, you can make an informed decision and choose a diamond that meets your personal preferences and budget while maximizing its visual appeal.
Ultimately, the beauty of a diamond lies in the eye of the beholder. Whether you prioritize a dazzling, colorless appearance or value the uniqueness of inclusions, selecting a diamond that speaks to you and evokes a sense of joy and admiration is the key to finding the perfect gem that will be cherished for a lifetime.…