GIA Diamond Quality | The Diamond 4Cs
When it comes to purchasing a diamond, understanding its quality is essential to ensure a confident and informed decision. The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) is recognized as the foremost authority in diamond grading and certification. In this article, we delve into the in-depth details of the GIA Diamond Grading System, focusing on the GIA 4Cs (Color, Clarity, Cut, and Carat Weight) and specifically exploring the GIA 4Cs Color Scale, from D to Z. By comprehending the GIA’s rigorous standards, readers can feel well-informed and secure in their diamond purchases.
The Original Source for Diamond Grading: GIA
Established in 1931, the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) is a non-profit organization dedicated to research, education, and the standardization of diamond grading practices. The GIA developed the internationally recognized 4Cs grading system, which revolutionized the diamond industry and provided consumers with a reliable framework to assess diamond quality.
The GIA 4Cs of Diamond Quality
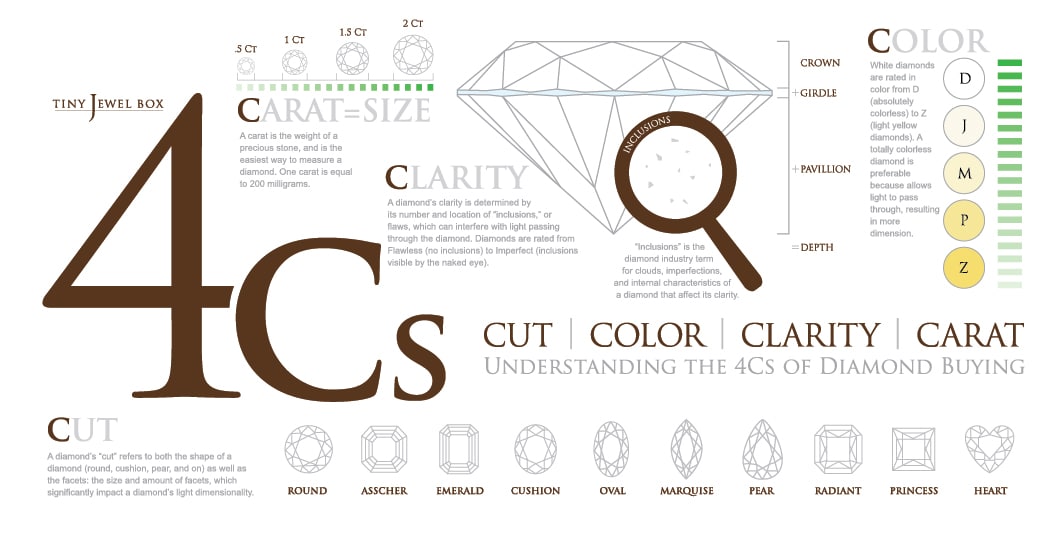
Color:
The GIA color scale ranges from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown), representing the absence or presence of color within a diamond. D is the highest color grade, indicating a diamond that is colorless and allows the maximum amount of light to pass through.
As the color grade progresses from D to Z, the presence of yellow or brown tints becomes more noticeable. However, it’s worth noting that the subtle color differences between adjacent grades may not be easily distinguishable to the untrained eye. The GIA’s strict grading standards ensure accurate and consistent color grading, providing consumers with confidence in their diamond selection.
Clarity:
Diamond clarity refers to the presence of internal and external characteristics, known as inclusions and blemishes, respectively. The GIA evaluates clarity on a scale ranging from Flawless (no visible inclusions or blemishes under 10x magnification) to Included (inclusions visible to the naked eye).
The GIA’s comprehensive clarity grading system allows consumers to assess the visibility and impact of a diamond’s inclusions. Diamonds with higher clarity grades exhibit exceptional transparency and are highly sought after for their brilliance. However, it’s important to note that many inclusions are microscopic and do not affect the beauty or durability of a diamond.
Cut:
The cut of a diamond refers to its proportions, symmetry, and polish, all of which determine how light interacts with the stone. The GIA assesses cut based on various factors, including brightness, fire, and scintillation.
The GIA grades cut quality as Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair, or Poor. Diamonds with excellent or very good cut grades reflect light optimally, resulting in exceptional brilliance and sparkle. Cut is often considered the most important factor in determining a diamond’s overall beauty, as it directly affects its light performance.
Carat Weight:
Carat weight measures a diamond’s size, with one carat equal to 200 milligrams. The GIA uses precise measurements and scales to determine a diamond’s carat weight accurately.
While carat weight is important, it is crucial to consider it in conjunction with the other three Cs (color, clarity, and cut) to fully assess a diamond’s quality. Factors such as the diamond’s proportions and cut quality can impact its visual appearance, making it possible for a slightly smaller diamond to exhibit more brilliance than a larger one.
Shopping Tips for Buying GIA-Certified Diamonds
Research and Education: Before making a diamond purchase, take the time to educate yourself about the 4Cs and the GIA grading system. Understand how each factor impacts a diamond’s quality and price. This knowledge will empower you to make informed decisions and ensure that you get the best value for your investment.
Choose GIA-Certified Diamonds: When buying a diamond, always look for those accompanied by GIA certification. GIA certificates are recognized and trusted worldwide for their accuracy and unbiased grading. They provide detailed information about the diamond’s 4Cs, ensuring transparency and authenticity.

Set Priorities: Determine which of the 4Cs are most important to you based on your preferences and budget. If color is a priority, focus on diamonds with higher color grades (D-F). If brilliance and sparkle are paramount, emphasize cut quality. Setting clear priorities will help you narrow down your options and find the perfect diamond for your needs.
Consider the Diamond’s Purpose: Think about the intended use of the diamond. If it’s for an engagement ring or a piece of jewelry that will be frequently worn, you may want to prioritize durability and choose a diamond with a higher clarity grade. If it’s for a decorative or occasional wear piece, you might have more flexibility in terms of clarity.
Compare and Contrast: Don’t settle for the first diamond you come across. Explore different options and compare diamonds with similar specifications. Look for variations in color, clarity, cut, and carat weight to find the best balance that suits your preferences and budget.
Seek Professional Guidance: Consult with a reputable jeweler or gemologist who can provide expert advice and guidance. They can help you navigate the complexities of diamond buying, explain the nuances of GIA grading, and assist you in finding the right diamond that meets your criteria.
Conclusion
The GIA Diamond Grading System, with its emphasis on the 4Cs (Color, Clarity, Cut, and Carat Weight), serves as the industry standard for evaluating diamond quality. The GIA’s rigorous grading standards and commitment to accuracy provide consumers with confidence and assurance when making diamond purchases. The GIA 4Cs Color Scale, ranging from D to Z, enables buyers to assess the presence or absence of color within a diamond. The color grading ensures consistency and precision, allowing consumers to select diamonds that meet their preferences and desired visual effect.
Diamond clarity, evaluated on a comprehensive scale by the GIA, provides insight into the presence and visibility of inclusions and blemishes. The grading system enables buyers to make informed decisions based on the visibility and impact of these characteristics.
Cut, another vital component of diamond quality, determines how well a diamond interacts with light. The GIA’s cut grading ensures that buyers can identify diamonds with exceptional brilliance, fire, and scintillation.
While carat weight measures a diamond’s size, it’s crucial to consider it in conjunction with the other three Cs to fully evaluate a diamond’s quality. The GIA’s precise measurements and accurate carat weight determination provide buyers with reliable information.
The GIA’s expertise, industry-leading standards, and commitment to consumer education make their diamond grading system the ultimate resource for assessing diamond quality. By familiarizing themselves with the GIA 4Cs Color Scale and the overall GIA Diamond Grading System, buyers can make well-informed decisions, secure in the knowledge that their diamond purchase is of the highest quality and value.…